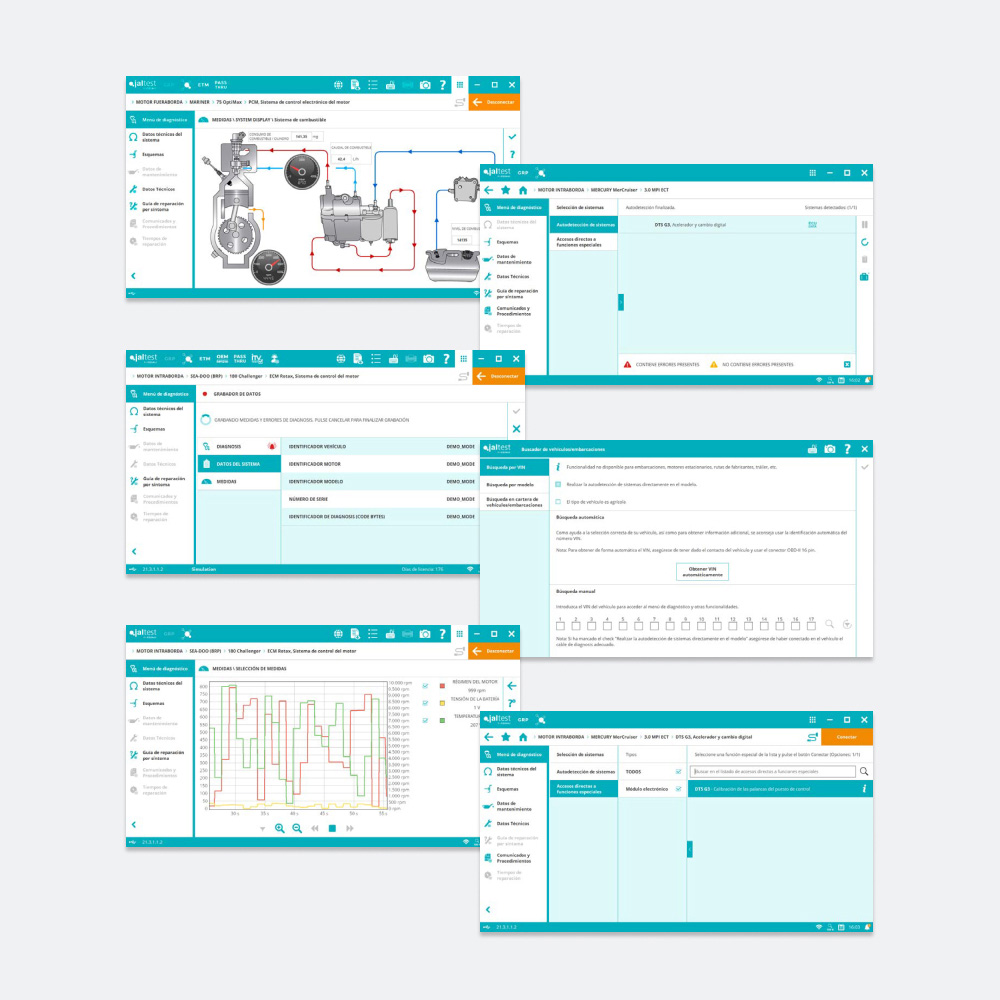
When it comes to diagnosing issues with marine vessels, understanding what certain fault codes mean and which parts they are related to is essential in being able to repair modern-day engines. It’s no longer the case that you can repair an engine with a set of screwdrivers and a service manual. With the level of complexity and number of ECUs in today’s inboard marine engines, you need a diagnostic tool like Jaltest to be able to connect to the engine’s ECUs, see what’s wrong and then perform the required repairs like for example, replacing and calibrating a new component.
In this article, we’ll be discussing why fault codes are important and outlining some of the most common marine vessel fault codes that you should be aware of if you’re a marine technician.
What are fault codes?
Fault codes, or diagnostic trouble codes (DTC), are codes that are stored in the ECU which correspond to a specific malfunction that has occurred within an engine. Technicians can see all of the fault codes stored on the engine’s ECU by plugging a diagnostic tool into the onboard ports and then running a system scan, which looks at all of the ECUs connected to the engine.
Unlike some other tools, Jaltest uses the same fault codes as the manufacturer, which means that it makes your life as a repairer so much easier, having a universally understood code that you can obtain information from or give to the dealer.
How to read fault codes?
The first number in the fault code tells you if the error is manufacturer-specific or if it’s a generic code, applicable to all systems. The last three numbers give you more information regarding the specific electrical circuit and system.
To get further information about what exactly has failed, Jaltest users have access to fault code descriptions, which give a brief description of what the fault is, and what system it pertains to. These fault code descriptions are incredibly user-friendly and make the process of diagnosing faults much easier.
Common fault codes you should be aware of
Now that you know what fault codes are and how to read them, let’s look at some of the most common fault codes that occur in marine vessels across some of the most popular manufacturers, such as Volvo Penta, IVECO-FPT, and MAN.
 1DE2FF – Fuel Pressure (MPROP)
1DE2FF – Fuel Pressure (MPROP)
Visible fault – MIL warning light on
Possible causes:
- Leaks in the high-pressure system
- Injector jammed open
- Low efficiency of the high-pressure pump
- Leaking injector
- Clogged fuel filter
- Low-pressure pump pipes clogged
- Faulty fuel supply electric pump
Repair:
Check the following components:
- Injectors
- High-pressure pump
- High and low-pressure system pipes
- Electrical wiring
 8C:81 – 0C
8C:81 – 0C
Possible causes or system faults/reactions:
- High-pressure circuit fuel leakage
- Injector jammed in fuel passage open position
- MPROP adjuster open movement jammed
- Faulty high-pressure pump
- MPROP regulator jammed
Recommended repair:
- Check fuel feed system
- Check hydraulic and mechanical efficiency of injectors
- Check efficiency of the MPROP adjuster
- Check efficiency of the high-pressure pump
- Check rail pressure sensor
- Check MPROP regulator and replace it if required
- Check fuel feed system and replace the high-pressure pump if required
- Check faulty fuel feed system (fuel pump and filter jammed)
- Check fuel return (possible pump issue)
- Check overpressure valve
- Check blockage with pick up
- Check the high-pressure system. Replace the high-pressure pump if required
Notes:
- Fuel management and pressure failure in rail
- Possible pressure relief valve fault
- 300 bar idle – 1300 bar full load
 3775-2 – Fuel supply pressure too low
3775-2 – Fuel supply pressure too low
Monitoring strategy:
- Monitoring whether fuel supply pressure is in the normal range
Effect of fault:
- The engine may stop, possibly lack of power
Consequential fault:
- Possibly SPN 3775-2. 3776, 3779
Cause of fault:
Fuel supply pressure is too low because:
- Tank breather blocked
- Pre-filter blocked
- Loose contact on the signal line
- Air in the system
- Fuel pressure at high-pressure pump feed too low due to defective pre-supply pump
- Fuel system ran dry due to leakage when the engine was stationary
 8204 fmi 3 – Rail pressure: injection shutdown
8204 fmi 3 – Rail pressure: injection shutdown
SPN 609 CAN MODULE 1
Fault display:
- Central fault lamp shows steady red light whilst driving and when stationary (priority 2)
Monitoring strategy:
- Monitoring for busoff state, CAN module 1
Effect of fault:
- EDC control unit goes into “Stand-alone mode” (i.e. engine cannot be accelerated beyond idling speed)
Fault entries in other control units:
- Yes, the vehicle management computer
Test:
- EDC control unit
- Vehicle management computer
- M-CAN databus
Correcting the fault:
- Check the electrical power supply
- Check lines
- Check plug connectors
- At approx. 0 Ω, short-circuit from CAN-H to CAN-L
- Fit a new control unit or vehicle management computer if no faults can be detected
 EMS P228F00
EMS P228F00
(Fuel pressure controller adjustment value saturated high)
Fuel Pressure Regulator 1 Exceeded Learning Limits – Too High
Check:
- Leaking Fuel Pressure Release Valve
- Leaking High-Pressure Fuel System
- High Fuel Pressure Pump
- Fuel Pressure Regulator
- Low Fuel Pressure System, fuel supply
Check components:
- Y143 – Pressure limiting valve
- M15 – Fuel priming pump
- B222 – Rail pressure sensor
 PSID 96 – Rail pressure system
PSID 96 – Rail pressure system
Possible cause:
- Fuel rail pressure sensor
- Fuel control unit closed
- Injectors
Action:
- Fault trace the fuel system
- Checks on PID 94 PID 164 (Please see attached files)
- Check possible leaks in the high-pressure lines
Fault trace fuel system – Carry out checks:
- Clogged fuel filter
- Air or leak in the fuel system
- Faulty bypass valve
- Worn out fuel pump
- Mechanical fault in the sensor
Faulty injection control:
- Check wiring
- Check the injection control pressure regulator
- Faulty data
- Faulty sensor
- Possible internal fault in the control unit
Pressure release valve:
- Faulty signal from rail sensor
- Fuel control unit closed
- Overpressure valve stuck open
- Pressure regulation not working
I have my fault code – now what?
So, now you have a top-level understanding of what the problem is from looking at the error codes and fault code descriptions. Next, you want to move into more detailed troubleshooting of the fault. Well, Jaltest not only allows you to read and delete these error codes but from there, you can also then see recommended fault code troubleshooting steps and possible error causes, linking directly to the actions to be carried out (testing procedures, component replacement, etc.).
In addition, you have access to a whole suite of dealer-level technical information such as detailed interactive wiring diagrams, system operational diagrams, component locations, and vessel technical data, such as tightening torques, reference measurements etc. Having all of this information at your fingertips means that you have everything you need to carry out the repair process and be more efficient in doing so.
Final thoughts
It’s safe to say fault codes are unavoidable when it comes to diagnosing and repairing modern-day marine vessels. So having the right diagnostics tool is a must for interpreting what these error codes mean.
That’s why many technicians rely on Jaltest – the No.1 multi-brand diagnostics tool for the marine market, which allows testing of engines, helm controls, drive controls and powertrain and much more across 84+ brands and 1,499 models.
So, if you’re looking for a dealer-level diagnostics tool, book a free demonstration today with one of our team at Eclipse to see how Jaltest can help your business.